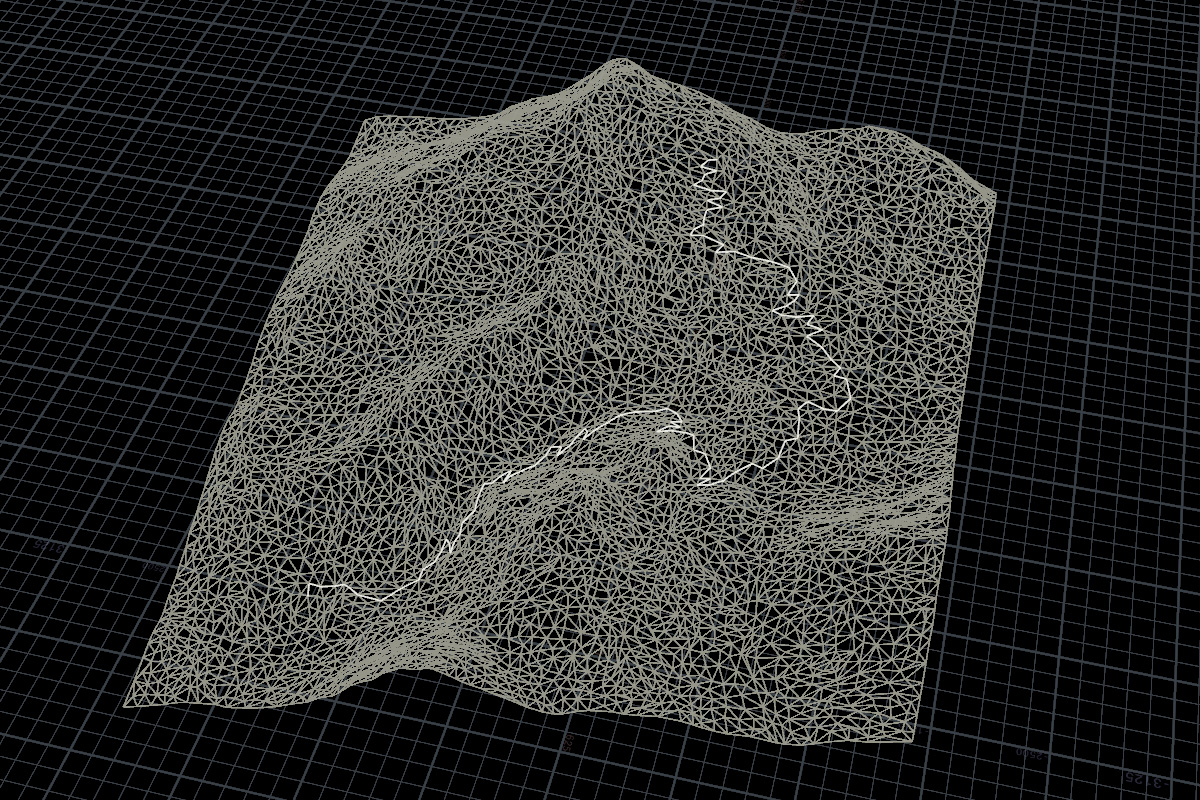
A-Starアルゴリズムをベースに、勾配コストを追加したアルゴリズム。
Input0にConvertline SOPでポリライン化した地形を、Input1に始点と終点を含むポリラインを差す。
// RunOver: Detail
// input0: Polyline Graph
// input1: Polyline
vector start = point(1, "P", 0);
vector goal = point(1, "P", 1);
// 始点
vector cross;
vector uv;
vector origin = start + set(0, 1, 0) * 50000;
vector dir = set(0, -1, 0) * 100000;
int hitId = intersect(1, origin, dir, cross, uv);
if(hitId >= 0)
i@startId = nearpoint(0, cross);
else
i@startId = nearpoint(0, start);
// 終点
origin = goal + set(0, 1, 0) * 50000;
dir = set(0, -1, 0) * 100000;
hitId = intersect(1, origin, dir, cross, uv);
if(hitId >= 0)
i@goalId = nearpoint(0, cross);
else
i@goalId = nearpoint(0, goal);ポイントから隣接するエッジからの情報を格納する。ポイントから隣接ポイントまでの傾斜コストのリストも事前計算しておく。
// RunOver: Points
// 隣り合うポイント
int neighbours[] = neighbours(0, @ptnum);
i[]@connectedPoint = neighbours;
// 隣り合うポリライン
int connectedPrim[] = pointprims(0, @ptnum);
i[]@connectedPrim = connectedPrim;
// ポリラインの長さ
f[]@distance;
for(int i = 0; i < len(neighbours); i++)
{
vector pos = point(0, "P", neighbours[i]);
f[]@distance[i] = length(pos - @P);
}
// 傾斜コスト
float amount = `chs("../slopeAmount")`;
for(int i = 0; i < len(connectedPrim); i++)
{
int pts[] = primpoints(0, connectedPrim[i]);
vector p0 = point(0, "P", pts[0]);
vector p1 = point(0, "P", pts[-1]);
vector diff = normalize(p1 - p0);
vector h = normalize(set(diff.x, 0, diff.z));
float theta = acos(dot(h, diff)); // 角度Θ
// 勾配コスト
f[]@slopeCost[i] = pow(theta / (PI/2), amount);
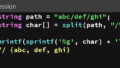
}Python SOPで経路探索を記述する。
#
# A*の経路探索
#
slopeLevel = `chs("../slopeAmount")`
node = hou.pwd()
geo = node.geometry()
import time
import math
# Start
start_time = time.time()
# 地点クラス
class Node:
def __init__(self, connect, dist, slopeCost):
self.index = -1
# 直前のインデックス
self.prevPt = -1
# 探索済みフラグ
self.flag = 0
# コスト(一応大きな数を入れておく)
self.totalCost = 100000000.0
# 接続する道路
self.connect = connect
# 道路のコスト(距離)
self.dist = dist
# 推測コスト
self.heuristicCost = 0.0
# スコア(それまでのコスト+推測コスト+勾配コスト)
self.score = 0.0
# 座標
self.position = hou.Vector3()
# 勾配コスト
self.slopeCost = slopeCost
start = geo.intAttribValue('startId')
goal = geo.intAttribValue('goalId')
# ルートリスト
openList = []
# ポイント総数
nPoints = len(geo.points())
# 分岐するルートと距離の情報を格納する
connect = []
dist = []
position = []
normal = []
slopeCost = []
for pt in geo.points():
connect.append(pt.intListAttribValue("connectedPoint"))
dist.append(pt.floatListAttribValue("distance"))
position.append(pt.position())
slopeCost.append(pt.floatListAttribValue("slopeCost"))
#print position
# ノードクラスのリストを初期化
node = []
for i in range(nPoints):
node.append(Node(connect[i], dist[i], slopeCost[i]))
node[i].index = i
node[i].position = position[i]
#
# 計算開始
#
# startからのルートをリストに入れる
node[start].totalCost = 0.0
node[start].heuristicCost = (node[goal].position - node[start].position).length()
node[start].score = node[start].totalCost + node[start].heuristicCost;
node[start].prevPt = start
node[start].flag = 1
openList.append(start)
# 比較用のクラスリスト
classList = []
classList.append(node[start])
#
# ループ処理
#
# リストが空になるまで続ける
while len(openList) > 0:
# ラムダ式で昇順に並べ替え
classList = sorted(classList, key=lambda x: x.score)
currentPt = classList[0].index
#print "current:" + str(currentPt) + ":" + str(node[currentPt].score)
# removeはリスト要素を値で削除
openList.remove(currentPt)
# popはリスト要素をインデックスで削除
classList.pop(0)
for j in range(len(node[currentPt].connect)):
nextPt = node[currentPt].connect[j]
# 距離のコスト
cost = node[currentPt].totalCost + node[currentPt].dist[j]
# 進行方向の勾配コスト
slopeCost = node[currentPt].slopeCost[j]
slopeCost = math.pow(slopeCost, slopeLevel) # 指数で増減させる
slopeCost *= node[currentPt].dist[j] # 道の距離に掛ける
# もし探索済みで、新しいルートのほうがコストが低い場合は更新する
if node[nextPt].flag == 1:
if cost + slopeCost < node[nextPt].totalCost:
node[nextPt].totalCost = cost + slopeCost
node[nextPt].score = node[nextPt].totalCost + node[nextPt].heuristicCost
node[nextPt].prevPt = currentPt
else:
node[nextPt].totalCost = cost + slopeCost
node[nextPt].heuristicCost = (node[goal].position - node[nextPt].position).length()
node[nextPt].score = node[nextPt].totalCost + node[nextPt].heuristicCost
node[nextPt].prevPt = currentPt
node[nextPt].flag = 1
openList.append(nextPt)
classList.append(node[nextPt])
# ゴールだった場合
if nextPt == goal:
#print "A-star::num search:" + str(i)
break
#二重ループをブレイクする処理
else:
continue
break
#print openList
# ルートを検索
if node[goal].prevPt != -1:
route = []
pt = goal
count = 0
while(pt != start):
route.append(pt)
pt = node[pt].prevPt
count = count + 1
if count > 1000:
print("loop!!")
break
route.append(start)
route.reverse()
#print route
# Detailに保存
geo.addArrayAttrib(hou.attribType.Global, 'route', hou.attribData.Int, 1)
geo.setGlobalAttribValue('route', route)
geo.addAttrib(hou.attribType.Global, 'dist', 0.0)
geo.setGlobalAttribValue('dist', node[goal].totalCost)
geo.addAttrib(hou.attribType.Global, 'start', 0)
geo.setGlobalAttribValue('start', start)
geo.addAttrib(hou.attribType.Global, 'goal', 0)
geo.setGlobalAttribValue('goal', goal)
# End
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
print ("A-star_route::time:{0}".format(elapsed_time) + "[sec]")
# Debug
geo.addAttrib(hou.attribType.Point, 'cost', 0.0)
index = 0
for point in geo.points():
point.setAttribValue('cost', node[index].totalCost)
index = index + 1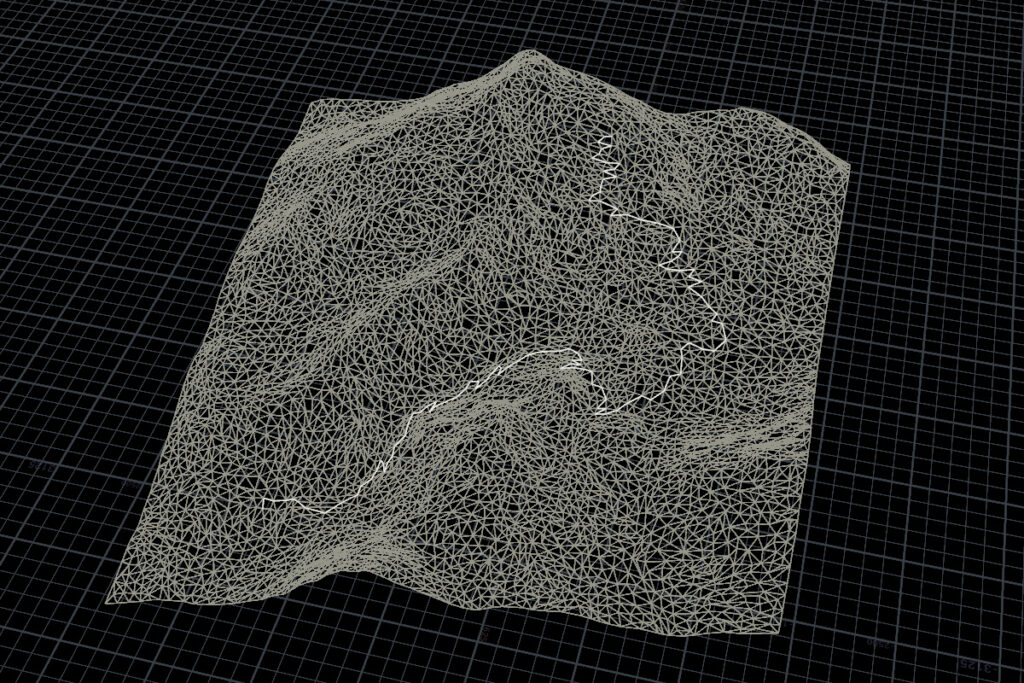
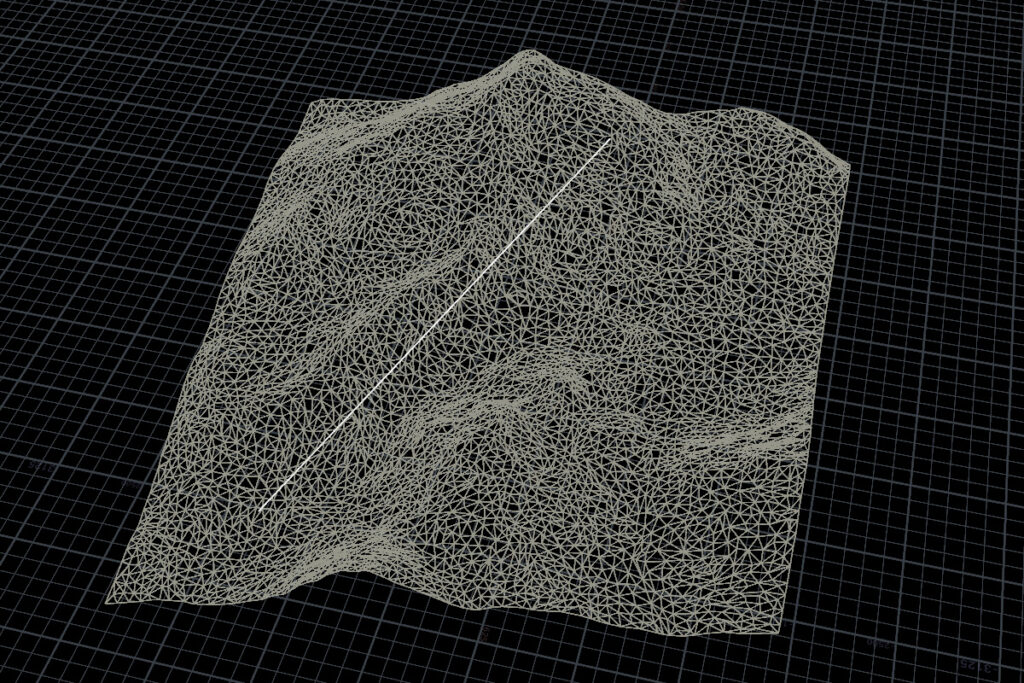
Python SOPの結果からラインを生成するVEXコード。
// RunOver: Detail
// input0: None
// input1: Python SOP
int route[] = detail(1, "route", 0);
int prim = addprim(0, "polyline");
for(int i = 0; i < len(route); i++)
{
vector pos = point(1, "P", route[i]);
int pt = addpoint(0, pos);
addvertex(0, prim, pt);
}ポイントリストのrouteからポリラインを取得するコード。
// RunOver: Detail
int route[] = detail(0, "route", 0);
int routePrim[];
for(int i = 0; i < len(route)-1; i++)
{
int pts[] = neighbours(0, route[i]);
int prims[] = pointprims(0, route[i]);
for(int j = 0; j < len(pts); j++)
{
if(pts[j] == route[i+1])
{
append(routePrim, prims[j]);
break;
}
}
}
i[]@routePrim = routePrim;環境:Houdini 19.5.752