環境:Houdini 19.5.752

曲率とは
曲率半径
曲線を局所的な円弧と見た場合の半径。
曲率
曲率半径の逆数になる。
パラメトリックUVで計算する
ポリラインの各ポイントの曲率を計算する。Resample SOP等でポリラインが均等なポイント配置になっている必要あり。前後のポイントを使って計算する。
//
// ポリラインの角ポイントの曲率を計算する
// Run Over: Primitives
//
float step = 5.0; // 曲率を計算する幅(片側)
int pts[] = primpoints(0, @primnum);
float curveLength = primintrinsic(0, "measuredperimeter", @primnum);
for(int i = 0; i < len(pts); i++)
{
vector pos = point(0, "P", pts[i]);
int index;
vector uv;
xyzdist(0, pos, index, uv);
// 端はクランプする
float prev_u = clamp(uv.x - (step / curveLength), 0, 1);
float next_u = clamp(uv.x + (step / curveLength), 0, 1);
vector p0 = primuv(0, "P", index, set(prev_u, 0));
vector p1 = point(0, "P", pts[i]);
vector p2 = primuv(0, "P", index, set(next_u, 0));
// 弦長
float chord_length = length(p2 - p0);
// p1から一番近いP0-P2上の点
vector min_pos = p0 + dot((p1 - p0), normalize(p2 - p0)) * normalize(p2 - p0);
// 矢高
float arc_height = length(min_pos - p1);
// ほとんど矢向が0に近い場合は無限半径(=0)、またはほぼ直線とみなす
if(arc_height < 0.0001)
{
setpointattrib(0, "__radius", pts[i], 0.0);
setpointattrib(0, "__theta", pts[i], PI);
setpointattrib(0, "__curvature", pts[i], 0.0);
}
else
{
// 半径
float radius = (pow(chord_length,2) / 4 + pow(arc_height, 2)) / (2 * arc_height);
float theta = 2 * asin(chord_length / (2 * radius));
if(theta > radians(0.0))
{
setpointattrib(0, "__radius", pts[i], radius);
setpointattrib(0, "__theta", pts[i], theta);
setpointattrib(0, "__curvature", pts[i], 1.0/radius);
}
}
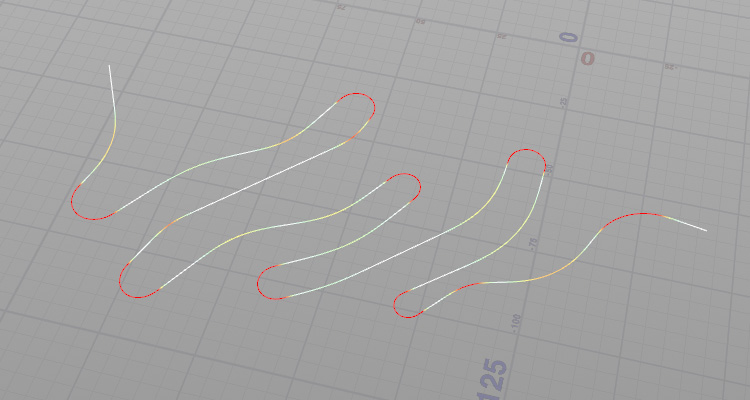
}曲率を視覚化する

曲率を彩度のグラデーションにする。曲率を計算したポリラインにWrangle SOPを続けてつなぐ。
//
// 曲率に色をつけて視覚化する
// Run Over: Points
//
float minRadius = 20; // 上限の最小曲率半径(m)(赤く表示される値)
float maxCurvature = 1.0/minRadius; // 上限の曲率
float curvature = f@__curvature;
float ratio = clamp(curvature/maxCurvature, 0, 1.0);
float hue = ratio * 0.5 * -1 + 0.5;
vector color = hsvtorgb(hue, ratio, 1.0);
@Cd = color;端点の曲率に対処する
端点には片側のデータしかないので、曲率の計算ができず直線の扱いになってしまう。これを回避するためには、端点の延長線上にポイントがあるとみなして計算する。
//
// ポリラインの角ポイントの曲率を計算する
// Run Over: Primitives
//
float step = 5.0; // 曲率を計算する幅(片側)
int pts[] = primpoints(0, @primnum);
float curveLength = primintrinsic(0, "measuredperimeter", @primnum);
for(int i = 0; i < len(pts); i++)
{
vector pos = point(0, "P", pts[i]);
int index;
vector uv;
xyzdist(0, pos, index, uv);
// 端はクランプする
float prev_u = uv.x - (step / curveLength);
float next_u = uv.x + (step / curveLength);
vector p0 = primuv(0, "P", index, set(prev_u, 0));
vector p1 = primuv(0, "P", index, uv);
vector p2 = primuv(0, "P", index, set(next_u, 0));
// p0またはp2が端を越えた場合
if(prev_u < 0)
{
float extra_dist = prev_u * curveLength;
vector N = point(0, "N", pts[0]);
vector P = point(0, "P", pts[0]);
p0 = P + N * extra_dist;
}
if(next_u > 1.0)
{
float extra_dist = (next_u - 1.0) * curveLength;
vector N = point(0, "N", pts[-1]);
vector P = point(0, "P", pts[0-1]);
p2 = P + N * extra_dist;
}
// 2次元平面上の曲率を求めるなら高さを0にする
//p0.y = 0;
//p1.y = 0;
//p2.y = 0;
// 三角形の面積
float area = length(cross((p0 - p1), (p2 - p1))) * 0.5;
// 3辺の長さ
float a = length(p2 - p1);
float b = length(p0 - p2);
float c = length(p0 - p1);
// 外接円の半径
float radius = (a * b * c) / (4.0 * area);
// 弦長と半径から中心角を計算する
float chord_length = length(p2 - p0);
float theta = 2 * asin(chord_length / (2 * radius));
if(theta > radians(0.0))
{
setpointattrib(0, "__radius", pts[i], radius);
setpointattrib(0, "__theta", pts[i], theta);
setpointattrib(0, "__curvature", pts[i], 1.0/radius);
}
}